It is already known that, from the beginning of this year, specialists in construction, architecture and urbanism can use the qualified electronic signature to sign the documents that are sent to the competent authorities and institutions in issuing approvals, agreements and authorizations. A much simpler, faster and more efficient option than a handwritten signature and a professional stamp or initial.
But is this necessary? Or, in other words, why would professionals in these fields turn to a qualified electronic signature, if they have done well so far with the classic method, pen on paper? In short, we could answer these questions with another one – why just “handle” when you could make your work (and life) much easier by enjoying all the benefits of a qualified electronic signature certificate?
1. A qualified electronic signature has implicit legal value
According to the EU eIDAS Regulation no. 910/2014, the qualified electronic signature is the only type of electronic signature that implicitly has the equivalent legal effect of a handwritten signature. Why does this matter? Because the qualified signature, according to the European norms that our country is obliged to respect, meets certain conditions related mainly to data security, ensuring a direct and undoubted link between a person’s real identity and his/hers electronic identity.
2. The qualified electronic signature cannot not be falsified…
Unlike the handwritten signature – which can be easily imitated and can hardly be proved as belonging to a certain person (only if you do not have at hand a specimen signature with which to compare it and possibly some graphological knowledge such as to do this) – the qualified electronic signature cannot be forged.
3. … and can be extremely easily verified
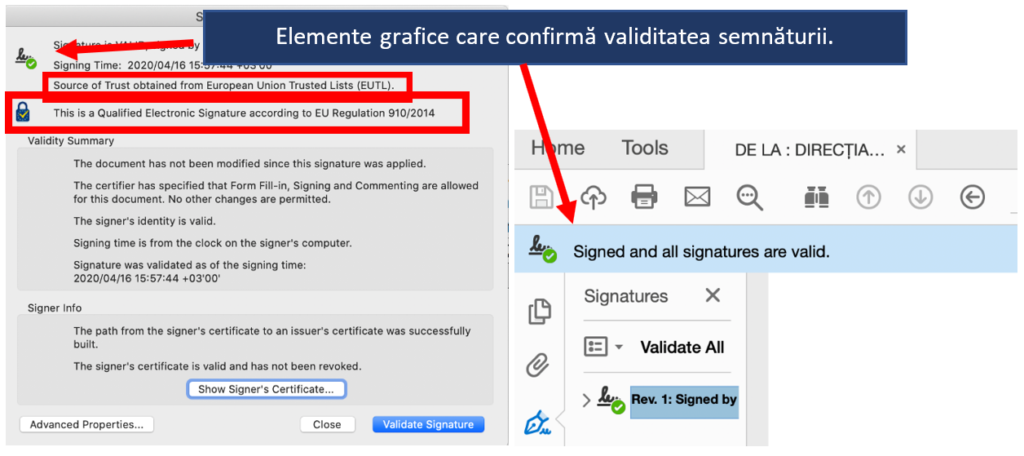
A document signed with a qualified certificate for electronic signature is impossible to falsify, you know for sure who the signing person is and you can check this very easily and quickly, in the free Adobe Acrobat Reader application. The app knows how to do the verification automatically, accessing the existing infrastructure at the level of all EU countries – known as the EU Trusted List of Trust Service Providers (EUTL) – where companies offering qualified signature services are shown.
Specifically, with a single click on the qualified signature in the document opened in Adobe Acrobat Reader (and then on Signature Properties), its validity will be confirmed by:
- indication of the source of the information used to validate the signature: “Source of Trust obtained from the European Union Trusted Lists (EUTL)”;
- the European Union’s trust mark (the blue padlock with the EU flag) and the identification of the electronic signature as qualified;
- green check mark and the text “Signed and all signatures are valid”.
4. Qualified electronic signature = high security
The qualified certificates for electronic signature are issued by qualified trust service providers registered in the EUTL and certified according to eIDAS (as is certSIGN), only after completing the procedure of proving and verifying the identity of the natural or legal persons requesting them, a mandatory procedure by Regulation 910/2014. This ensures that the electronic identity of the signatory is the same as the physical identity. In short, the signature is applied by the person who needs to, not someone else.
In addition, the actual signing process involves the use of a cryptographic device (token) and a unique PIN code, the signature being under the sole control of the signatory. Also, any modification of an electronically signed document is detectable. Thus, fraud attempts are completely eliminated.
And these are not the only advantages of using a qualified signature by specialists in construction, architecture and urbanism. In a further article we will present information at least as interesting as the one in this material – about the simplicity of the signing steps, the possibility of including a time stamp in the signature and much more.
